Department of Nuclear Medicine & Positron Emission Tomography ❯ Our Services ❯ Nuclear Medicine
Nuclear medicine is used for detection of metabolic activities of organs and tissues. It can identify disorders such as coronary artery disease, metastatic lymph node localization, pulmonary embolism, gastro-intestinal bleeding and physiological organs impairment effectively.
How can Nuclear Medicine help patients?
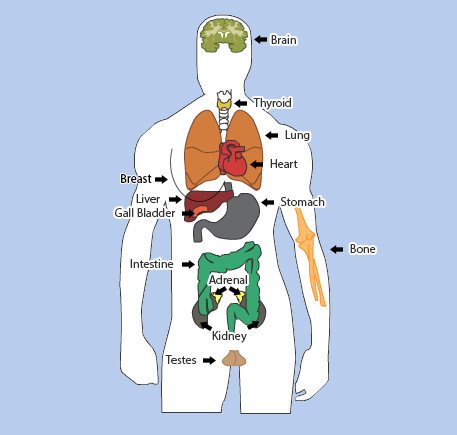
- Brain (cerebral perfusion scan)
- Thyroid (thyroid uptake, thyroid scan, thyrotoxicosis and thyroid cancer ablation)
- Lung (ventilation/ perfusion scan)
- Heart (myocardial perfusion scan)
- Breast (sentinel node mapping)
- Bone (bone scan, Sr-89 and Ra-223 treatment)
- Liver (liver scan and cancer treatment)
- Stomach (GE reflux and gastric emptying)
- Adrenal (iodocholesterol scan)
- Kidney (renal DTPA/MAG3 and DMSA scan)
- Intestinal (gastro-intestinal bleeding and protein losing enteropathy scan)
- Testes (testicular perfusion scan)
 Brain
Brain Perfusion Scan
Cisternogram (Cerebral Spinal Fluid Study)
Thyroid
Thyroid Scan and Thyroid uptake The human thyroid gland needs to make the thyroid hormone, which basically regulates the metabolic activities of the entire human body. When the gland is overactive, the patient may have heat intolerance, increased irritability, sweating, bowel movements, weight loss and increased awareness of heart beats. We can use iodine-131 for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. When there are lumps in the gland, it is sometimes useful to check if these lumps are overactive or underactive. Treatment for Thyrotoxicosis The ingestion of radioactive Iodine-131, which is concentrated in the thyroid gland will result in damage to and destruction of some of the cells of the thyroid. Thyroid Cancer Ablation Thyroid cancer may be mulitfocal, microscopically or macroscopically, in about 1/3 of the cases. After thyroidectomy, residual thyroid tissue or probable metastases, should be treated with radioactive on same line ablation. This may subsequently lower the tumour recurrence rate as well as later metastases. Hong Kong Sanatorium & Hospital is the first private hospital in Hong Kong which incorporates such a unique facility for thyroid cancer treatments. Lung
Pulmonary perfusion scan
Pulmonary perfusion and ventilation scan
Heart
Myocardial Perfusion Scan Myocardial Perfusion Scan is a well-known non-invasive means to detect the presence of coronary artery disease (CAD) as well as to assess the severity of CAD in relation to function. The heart receives life-giving blood from vessels called coronary arteries. If these arteries become partially blocked or narrowed by the accumulation of cholesterol or fat, the heart may not receive the amount of blood necessary for proper function. This narrowing of coronary arteries is often caused by atherosclerosis, one of the causes of a CAD. Symptoms include angina, fainting and panting and in serious case, death. Early detection of CAD is essential for better prognosis. Breast
Sentinel Node Mapping A sentinel node is the first lymph node to which cancer cells are most likely to spread from a primary tumor. Sentinel Node Mapping is a procedure using radioactive tracer to locate the sentinel node of Breast Cancer. Biopsy result of the sentinel node can help doctor to determine the stage of cancer and develop an appropriate treatment plan. Bone
Bone Scan Bone scintigraphy is highly effective to identify evidence of metastases and minor change in bone activity. The human skeleton needs phosphate as a substrate in metabolism. An area in the skeleton that works harder (with a higher metabolic activity) requires more phosphate. For example, when a tumour spreads to bone, the tumour cells disrupt the normal bone matrix organization. The human skeleton then reacts by trying to repair the damage. This repair needs more phosphate than normal bone metabolism. Different tumour cells can cause different rates of bone invasion and skeletal repair is likewise different. Even small repair can be detected and this is why bone scintigraphy can be very sensitive in the detection of early tumour invasion to bone before an apparent structural damage is seen on plain film radiographs. Early detection is important to controlling metastases. Radionuclide Therapy Strontium-89/Radium-223 Therapy for Bone Metastases The therapy specifically targets sites of metastatic disease in bone, known and unknown, simultaneously. Radionuclide Therapy relieves pain associated with bone metastases and acts as an effective adjunct therapy to arrest metastatic bone disease progression. In documented reports, patients experienced pain relief, and the majority had marked decrease in bone pain or became completely pain free. This therapy has fewer side effects. Liver
Liver scan
Yttrium-90 (Y-90) microspheres Selective Internal Radiation Therapy (SIRT) Y-90 SIRT is an internal radiation therapy for liver cancer. This therapy is suitable for the treatment of primary liver cancer or secondary liver tumors. The principle of SIRT is to take advantage of the physiological characteristics of the different blood supplies of tumor and normal liver. Usually about 80% of the blood supply of tumors is provided by the hepatic artery, while the portal vein provides most of the blood supply for normal liver tissue. If Y-90 microspheres are injected through the hepatic artery catheter, most of the Y-90 will preferentially enter and stay inside the tumor, thereby reducing damage to the normal liver. Y-90 microspheres generally lodge in the micro-vessels of the tumor, exerting localized radiation therapy. The β radiation inside human body can travel only up to a maximum of 11 mm, and will not cause potential harm to nearby people under normal circumstances. Stomach
Gastroesophageal Reflux Scan
Gastric Emptying Study
Gall Bladder
Hepatobiliary Scan
Adrenal
Adrenal Medulla MIBG Scan
Adrenal Cortex Iodocholesterol Scan Iodocholesterol Scan is helpful in evaluation of Cushing's syndrome. Kidney
Renal Scan This examination uses radiopharmaceuticals that are freely filtered (DTPA) or excreted (MAG3) by the kidneys. In this way we can assess the filtering function, drainage function, as well as blood flow and gross morphology (DMSA) of the kidneys. This test is also very useful in the evaluation whether the kidney arteries are the cause of high blood pressure in some patients. Intestine
Meckel's Scan
Gastro-Intestinal Bleeding Scan
Testes
Testicular Scan
|



