Department of Nuclear Medicine & Positron Emission Tomography ❯ Our Services ❯ Radionuclide Therapy
Radionuclide therapy utilizes biochemical molecule labeled with radioisotope to trace and treat targeted lesions by radiation with high linear energy transfer (such as α and β) at molecular distance. Because the biochemical properties of the molecule are highly specific to pathophysiology, radiation treatment is mostly delivered to abnormal tissues and effect on normal tissues is minimized.
With a comprehensive clinical setting, we are the only NMPET centre in Hong Kong that is capable of providing a one-stop full spectrum of radionuclide therapy services for treatment of cancers and other metabolic diseases. We understand that the quality of raw materials for radiopharmaceutical production and the safety in use are the most important to patients. To ensure radiopharmaceutical quality and safety, a series of stringent tests will be performed in QC laboratory by radiochemists before patient use; under the care of nuclear medicine specialists, radiographers and nurses in our private radiation isolation room can maximize patient safety and well-being during treatment. The current scope of treatment service includes Lutetium-177 (Lu-177) DOTA Conjugated peptides and Iodine-131 (I-131) MIBG for neuroendocrine tumor, Lutetium-177 PSMA for prostate cancer, Iodine-131 for thyrotoxicosis and thyroid cancer ablation, Yttrium-90(Y-90) Microspheres for liver cancer, Radium-223(Ra-223) Dichloride for bone metastases of prostate cancer and Strontium-89(Sr-89) Chloride for bone metastases palliation.
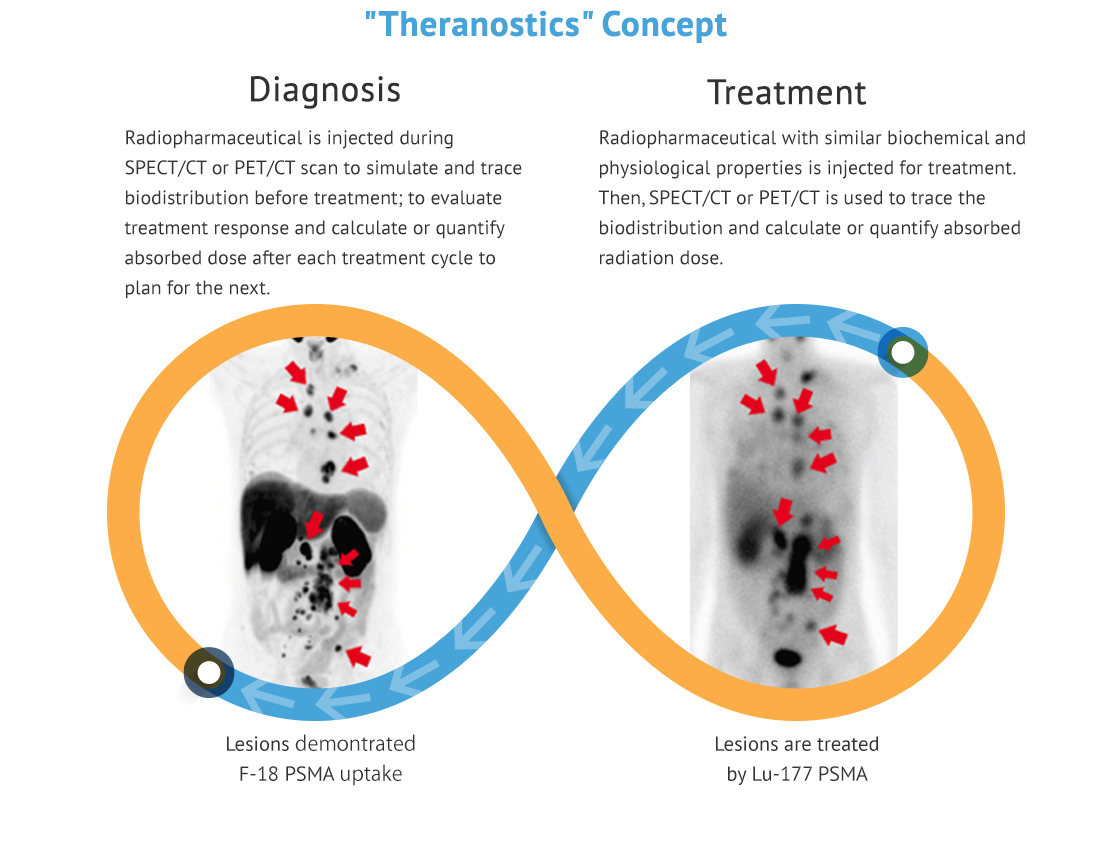
What is Theranostics?
Theranostics is a new concept in strategic management of cancer based on targeted molecular diagnostic imaging. Nuclear medicine and PET/CT, particularly with regard to applications in oncology, is currently one of the greatest components of the theranostics concept in clinical and research scenarios. In the field, theranostics refers to the use of radioactive compounds to image biologic phenomena by means of expression of specific disease targets such as cell surface receptors or membrane transporters, and then to use specifically designed agents to deliver ionizing radiation to the tissues that express these targets for imaging and therapy.
Firstly, various tracers with diagnostic radioisotopes (F-18, C-11, Ga-68, Tc-99m, I-123, etc.) are used for tomographic imaging (PET/CT and NM SPECT/CT) to perform cancer staging, trace metastases, simulate treatment and predict effectiveness. Subsequently, tracers with therapeutic radioisotopes (I-131, Lu-177, Y-90, Ra-223 and Sr-89, etc.) emitting high energy radiation can be applied to deliver highly specific treatment effect and visualize the distribution inside body.
The theranostics approach in Nuclear Medicine, SPECT/CT and PET/CT is useful to personalize management of diseases. Imaging parameters are incorporated into radionuclide therapy planning for improving patient selection, predicting response and toxicity and avoiding futile diagnostic examinations, which ultimately improve survival with better quality of life.
Firstly, various tracers with diagnostic radioisotopes (F-18, C-11, Ga-68, Tc-99m, I-123, etc.) are used for tomographic imaging (PET/CT and NM SPECT/CT) to perform cancer staging, trace metastases, simulate treatment and predict effectiveness. Subsequently, tracers with therapeutic radioisotopes (I-131, Lu-177, Y-90, Ra-223 and Sr-89, etc.) emitting high energy radiation can be applied to deliver highly specific treatment effect and visualize the distribution inside body.
The theranostics approach in Nuclear Medicine, SPECT/CT and PET/CT is useful to personalize management of diseases. Imaging parameters are incorporated into radionuclide therapy planning for improving patient selection, predicting response and toxicity and avoiding futile diagnostic examinations, which ultimately improve survival with better quality of life.

Common Radionuclide Therapies
Lu-177 PSMA Radionuclide Therapy for Prostate Cancer
This is a radionuclide therapy which utilizes radioligand to treat prostate cancer, particularly for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Lu-177 PSMA is a radiopharmaceutical which effectively destroys and kills prostate cancer cells. It consists of two elements:
1. PSMA, an antigen that binds to receptor on prostate cancer cell
2. Lu-177 is a β radiation emitter which delivers therapeutic effect
This radiopharmaceutical binds to the PSMA receptor, internalizes into prostate cancer cells and emits β radiation. The radiation has a high intensity and short travelling distance which deposits most of its energy in cancer cells. In the pathogenesis of prostate cancer cell, both primary and metastatic lesions express increased number of PSMA receptor. Cancer cells are destructed and killed after repeated irradiation.
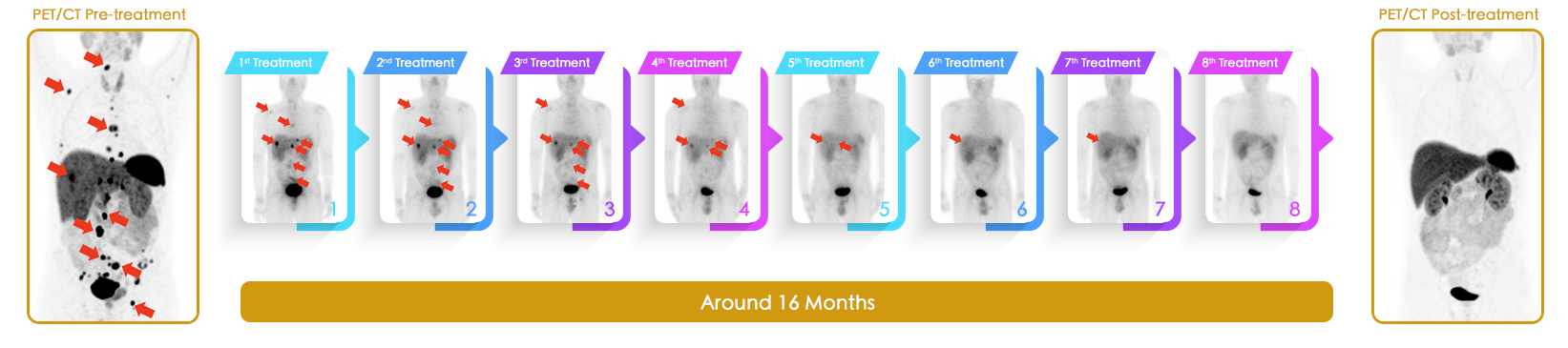
The treatment consists of 4-6 cycles normally, separated by 6-8 weeks between each cycle. F-18 PSMA and F-18 FDG PET/CT scans are necessary for disease evaluation before starting treatment. Nuclear Medicine specialist can evaluate treatment efficacy and prescribe Lu-177 PSMA dosage according to tracer avidity and distribution on PET/CT images. Since Lu-177 PSMA may temporarily decrease kidney function and cell regeneration rate, transient tiredness is expected with quick recovery.
This treatment provides an additional option for late stage prostate cancer patients. It can treat metastatic lesions as well as reduce bone pain due to osseous metastasis.

Improvement is seen in most of the lesions on F-18-PSMA PET/CT (indicated by red arrows) after Lu-177 PSMA radionuclide therapy. Lesions become metabolically inactive and less active on post-treatment scan.

Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) has significantly decreased after Lu-177 PSMA radionuclide therapy.
Lu-177 PSMA is a radiopharmaceutical which effectively destroys and kills prostate cancer cells. It consists of two elements:
1. PSMA, an antigen that binds to receptor on prostate cancer cell
2. Lu-177 is a β radiation emitter which delivers therapeutic effect
This radiopharmaceutical binds to the PSMA receptor, internalizes into prostate cancer cells and emits β radiation. The radiation has a high intensity and short travelling distance which deposits most of its energy in cancer cells. In the pathogenesis of prostate cancer cell, both primary and metastatic lesions express increased number of PSMA receptor. Cancer cells are destructed and killed after repeated irradiation.
The treatment consists of 4-6 cycles normally, separated by 6-8 weeks between each cycle. F-18 PSMA and F-18 FDG PET/CT scans are necessary for disease evaluation before starting treatment. Nuclear Medicine specialist can evaluate treatment efficacy and prescribe Lu-177 PSMA dosage according to tracer avidity and distribution on PET/CT images. Since Lu-177 PSMA may temporarily decrease kidney function and cell regeneration rate, transient tiredness is expected with quick recovery.
This treatment provides an additional option for late stage prostate cancer patients. It can treat metastatic lesions as well as reduce bone pain due to osseous metastasis.

Improvement is seen in most of the lesions on F-18-PSMA PET/CT (indicated by red arrows) after Lu-177 PSMA radionuclide therapy. Lesions become metabolically inactive and less active on post-treatment scan.

Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) has significantly decreased after Lu-177 PSMA radionuclide therapy.
Dual Tracer (C-11 Acetate & F-18 FDG) PET/CT & Y-90 Selective Internal Radiation Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
-
Pre-treatment Dual-tracer PET/CT
1. Identify metabolic heterogeneity factor
2. Classify cellular differentiation
3. Delineate radiosensitivities
- Liver tumor is inoperable because of its high metabolism and large size
- AFP is 2269 ng/ml


C-11 Acetate F-18 FDG
- Pre-treatment Tc-99m MAA SPECT/CT
- Predict distribution ratio of tumor-to-nontumor Y-90 microsphere on post-treatment Y-90 SPECT/CT
- Identify shunting to lungs or viscera
- Y-90 Liver Selective Internal Radiation Therapy (SIRT)
- Tc-99m MAA (Left) to simulate Yttrium-90 particle distribution
- Evaluate treatment feasibility
- Calculate Prescription Dose from dual tracer PET/CT
- Use PET/CT to scan Yttrium-90 particle distribution (Right)


Pre-treatment Tc-99m MAA SPECT/CT Post-treatment Y-90 PET/CT
- 3-month post-treatment dual tracer PET/CT
- Liver tumor metabolism and size are reduced
- AFP drops to 1206 ng/ml

C-11 Acetate F-18 FDG
Lu-177 DOTA-Conjugated Peptides Radionuclide Therapy for Neuroendocrine Tumor
This is a radionuclide therapy which utilizes peptide receptor to treat neuroendocrine tumor.
Neuroendocrine cells transmit nerve signals as well as secrete hormones. They are present in many organs such as thyroid, lung, intestines and pancreas etc. “Neuroendocrine tumor” is the name of its cancerous tissue. It is divided into functional and non-functional. The functional type secretes hormones and is symptomatic whereas the non-functional type does not and is asymptomatic.
Lu-177 DOTA conjugated peptide is a radiopharmaceutical which effectively destroys and kills neuroendocrine tumor cells. It consists of two elements:
1. DOTA conjugated peptide, a peptide that binds to somatostatin receptor on neuroendocrine tumor cell
2. Lu-177 is a β radiation emitter which delivers therapeutic effect
This radiopharmaceutical binds to the overexpressed somatostatin receptor, internalizes into neuroendocrine tumor and emits β radiation. The radiation has a high intensity and short travelling distance which deposits most of its energy in tumor cells. Tumor cells are destructed and killed after repeated irradiation. It can suppress tumor growth as well as reduce symptoms related to the disease, with improvement in overall survival at the same time.
The treatment consists of 4-6 cycles normally, separated by 6-15 weeks between each cycle. Ga-68 DOTA conjugated peptides and F-18 FDG PET/CT scans are necessary for disease evaluation before starting treatment. Nuclear Medicine specialist can evaluate treatment efficacy and prescribe Lu-177 DOTA conjugated peptide dosage according to tracer avidity and distribution on PET/CT images.
This treatment provides an additional option for patients with inoperable, metastatic or treatment resistant diseases. Improvement or stable disease is usually seen in majority of the patients who have received two or more cycles.
Neuroendocrine cells transmit nerve signals as well as secrete hormones. They are present in many organs such as thyroid, lung, intestines and pancreas etc. “Neuroendocrine tumor” is the name of its cancerous tissue. It is divided into functional and non-functional. The functional type secretes hormones and is symptomatic whereas the non-functional type does not and is asymptomatic.
Lu-177 DOTA conjugated peptide is a radiopharmaceutical which effectively destroys and kills neuroendocrine tumor cells. It consists of two elements:
1. DOTA conjugated peptide, a peptide that binds to somatostatin receptor on neuroendocrine tumor cell
2. Lu-177 is a β radiation emitter which delivers therapeutic effect
This radiopharmaceutical binds to the overexpressed somatostatin receptor, internalizes into neuroendocrine tumor and emits β radiation. The radiation has a high intensity and short travelling distance which deposits most of its energy in tumor cells. Tumor cells are destructed and killed after repeated irradiation. It can suppress tumor growth as well as reduce symptoms related to the disease, with improvement in overall survival at the same time.
The treatment consists of 4-6 cycles normally, separated by 6-15 weeks between each cycle. Ga-68 DOTA conjugated peptides and F-18 FDG PET/CT scans are necessary for disease evaluation before starting treatment. Nuclear Medicine specialist can evaluate treatment efficacy and prescribe Lu-177 DOTA conjugated peptide dosage according to tracer avidity and distribution on PET/CT images.
This treatment provides an additional option for patients with inoperable, metastatic or treatment resistant diseases. Improvement or stable disease is usually seen in majority of the patients who have received two or more cycles.




